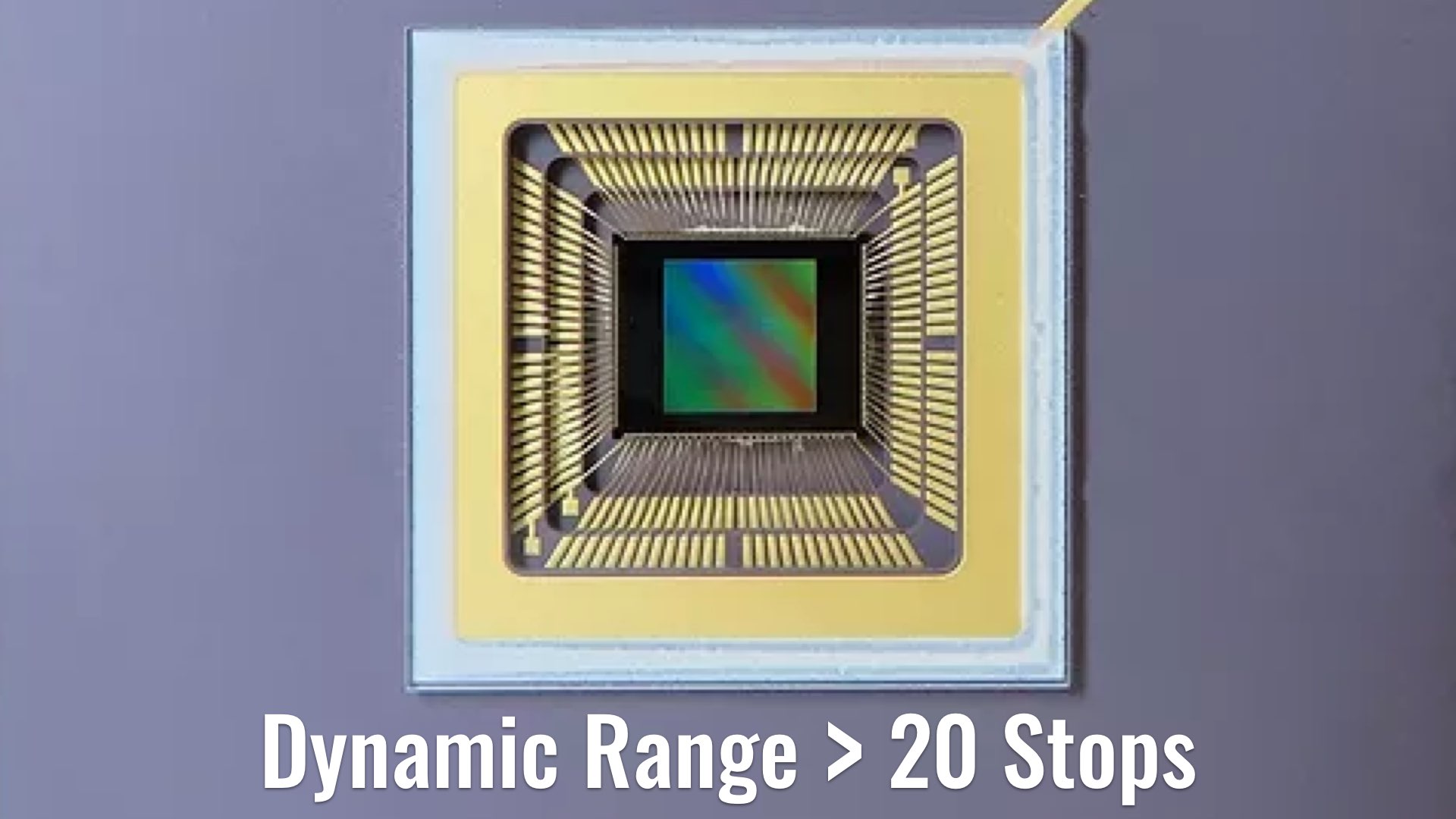
Gigajot announces its first QIS (Quanta Image Sensors) products, which the company calls the dawn of a new era in solid-state imaging. The new sensors can achieve a high dynamic range (above 20 stops), all in small pixel, high-resolution formats. Nerd alert!
Gigajot and QIS
Gigajot Technology Inc. was founded in 2017 as a spin-off from Dartmouth College to develop and commercialize the next generation of image sensors, quanta image sensors (QIS). QIS is the next generation of image sensors where high-speed single-photon detection is used to unlock new image capture capabilities for consumers and professionals not possible with today’s devices. The QIS over-samples the light field to generate binary measurements. Its single-photon sensitivity makes it an ideal candidate for the next-generation image sensor after CMOS. Gigajot says that its image sensors and cameras can be used in almost all the imaging systems that already use CMOS, sCMOS, CCD, EMCCD, and SPAD sensors for imaging. “Our image sensors and cameras can be used in various imaging applications, such as scientific & life science, medical, space, industrial, security & surveillance, defense, computational, automotive, photography, and cinematography” Gigajot states.

Our image sensors and cameras can be used in various imaging applications, such as scientific & life science, medical, space, industrial, security & surveillance, defense, computational, automotive, photography, and cinematography.
Gigajot
The first commercially available QIS
Gigajot announces its first QIS products, which the company calls the dawn of a new era in solid-state imaging. The new QIS products are capable of photon counting at room temperature while operating at full speed, and achieving high dynamic range – all in small pixel, high-resolution formats. With 5-10x read noise improvement over conventional small pixel image sensors, QIS enables imaging at ultra-low light levels not previously possible. For instance, the GJ00422 Quanta Image Sensor is a stacked BSI CMOS image sensor with a 4.2 megapixels (2048 x 2048) resolution. The 2.2 mm x 2.2 mm pixels are designed with Gigajot’s proprietary low-noise cluster-parallel readout structures to achieve reliable photon-counting sensitivity at room temperature, with industry-leading 0.27e- RMS read noise while operating at 4 MP resolution and 60 fps frame rate. The sensor utilizes an in-pixel dual-gain readout to achieve a single-exposure dynamic range of 100dB and more than 120dB with multi-exposure (above 20 stops of DR).
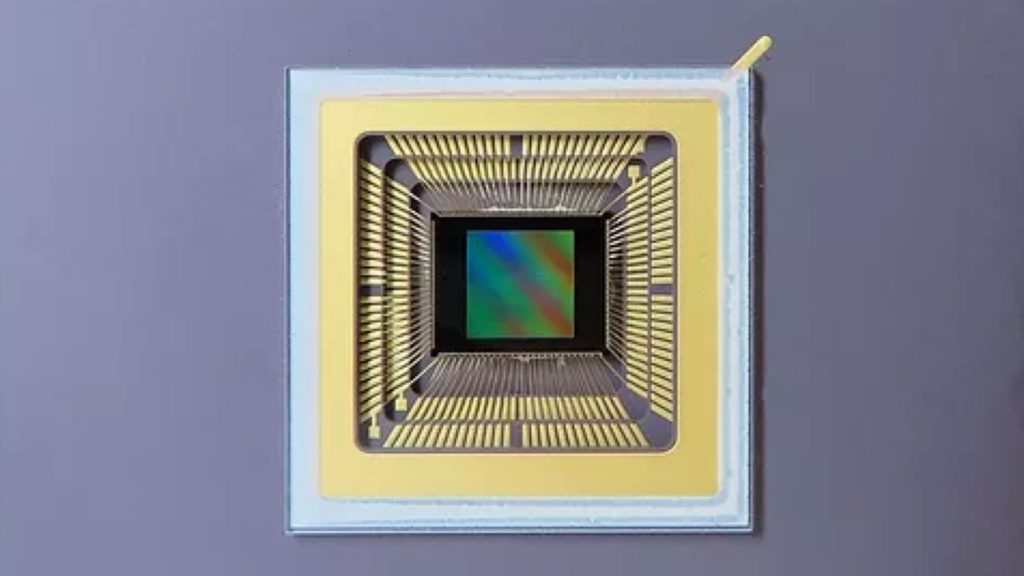
The dawn of a new era in solid-state imaging.
Gigajot
High Dynamic Range Imaging
Gigajot emphasizes that its proprietary imaging technologies, enable single-exposure high-dynamic-range imaging, without sacrificing low-light imaging performance or introducing additional motion artifacts:
- 100dB intra-scene dynamic range with 2.2μm pixels
- More than 120dB with multi-exposure
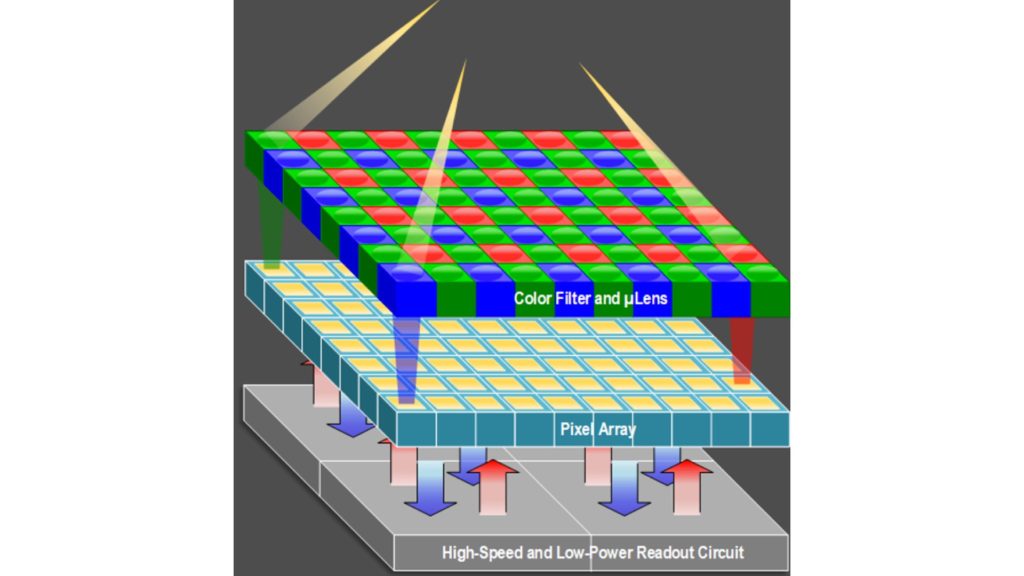
Main Features of the sensors
- Photon-counting sensitivity
- Accurate photon number resolving
- Stacked Backside Illuminated (BSI) CMOS process
- Excellent low-light imaging performance
- Deep sub-electron read noise
- Industry-leading low dark current
- High quantum efficiency
- High intra-scene dynamic range
- No avalanche gain, no deadtime, no high voltage
- On-chip programmable gain and ADC bit-depth
- Color and mono
- On-chip temperature sensor
- Patented pixel design and sensor architecture
Summary
After dusting off the geeky stuff, the main takeaways here that the QIS (Quanta Image Sensors) can be implemented into cameras for cinematography applications, in order to allow very high dynamic range imagery. That means, over 20-stops of DR. Of course it will take time till that happens. However, it’s always cool to explore new technologies regarding solid-state imaging.